
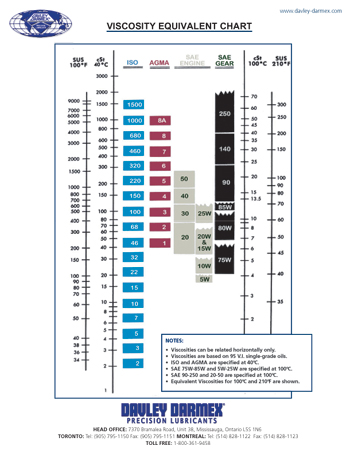
In the viscosity test, the fluid is placed in a specially designed glassware tube (Figure 1) and allowed to equilibrate at the desired temperature. Where μ is the dynamic viscosity, ρ is the density of the fluid, and ν is the kinematic viscosity. Kinematic viscosity is the ratio of dynamic viscosity to density: The (metric) units are g/(cm-s) or centipoise. Dynamic viscosity, or absolute viscosity, is a measure of the internal resistance of the fluid to motion. There are two types of viscosity - dynamic viscosity and kinematic viscosity. Typically, 100☏ and 210☏ are used for kinematic viscosity measurements in English units, and 40☌ and 100☌ are used for viscosity measurements using the metric system.
If the viscosity is measured using the metric system, then viscosity is reported in centistokes, or cSt.

If the temperature is measured in English units, then the units for viscosity are Saybolt Universal Seconds (SUS). Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow at a given temperature. Viscosity and the viscosity index are terms that are applied not only to quenchants, but also to many other areas in machining, lubrication, and tribology. I n this column, we will discuss the viscosity and viscosity index.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
